Hall sensor
Idea
Since wrong sensor readings can cause catastrophic failure of the TriPed, it is important to find out when such incorrect readings occur and to deal with them accordingly.
The general idea of error handling is to check each step of the SPI transfer from the beaglebone to the sensor for errors and to set the hardware interface into an error state, should the errors accumulate. The error types can also be weighted differently, depending on how critical they are in the operation of the motors.
Also, since higher-level control blocks depend on the lower levels, the state of the lower levels need to be broadcasted. This is done via ROS diagnostic topics.
What is tracked
The error handling of the controller can be seen in the following diagram: 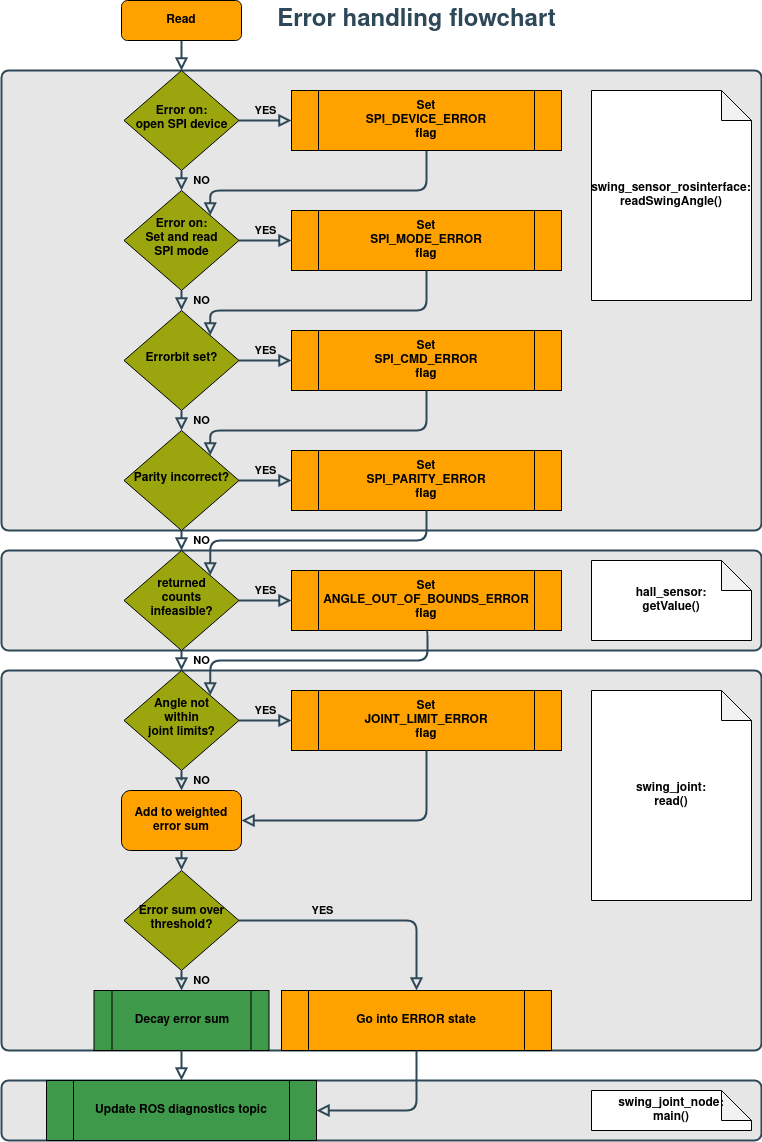
The error handling is present in each layer of the joint level controller. It begins in the lowest layer with the SPI transfer. The first check is, whether the SPI device can be opened. If this isn't the case, then a flag indicating so will be set. This flag is called SPI_DEVICE_ERROR and is set within the error parameter of the readSwingAngle function, which is a class variable of the HallSensor class. Furthermore, the SPI mode is set, read and if an error occurs the SPI_MODE_ERROR flag will be set. Then after the SPI transfer, the received message is checked for a set error bit, indicating a wrong last command frame to the sensor, and leading to the SPI_CMD_ERROR flag is set. The message is also checked for correct parity since a wrong parity indicates incorrectly transferred sensor values. A wrong parity is indicated by the SPI_PARITY_ERROR flag.
The next layer is the HallSensor class. There the returned counts of the sensor are checked for feasibility. This means the sensor returns a 16383 or 16384 value if it is not correctly connected to the beaglebone. Therefore a reading of said values leads to another error called ANGLE_OUT_OF_BOUNDS_ERROR. The hall sensor now calculates the sensor angle from the counts and gives it, together with all error flags, to the next higher layer.
Finally, in the read function of the SwingJoint class, the returned sensor angle is checked against the joint limits. Should the angle not be within the limits, specified in the joints.yaml file, the JOINT_LIMIT_ERROR flag is set.
Weighing the errors
The SwingJoint class contains the weighing functionality of the error handling system. For this an unsigned int stores the weighted sum of the previous reads. In the current read, this sum is increased by weights, depending on what error flags are set. Each flag can have a different weight to it. The values of the weights can be chosen arbitrarily, however, it is a good idea to set the values of the ANGLE_OUT_OF_BOUNDS_ERROR and the JOINT_LIMIT_ERROR to the error threshold, since they are a clear sign, that the sensor is not working as expected and an immediate switching into ERROR state is necessary. The other errors can be weighted far less aggressively, depending on how much they affect the operation of the joint.
What happens if an error occurs
The error gets detected, logged to the console, and then added to the weighted error sum. If this sum is larger than a specified threshold [see customization], then the system goes into an ERROR state. This leads to the following things happening: The SwingJoint::write() function will no longer write the command from the controller to the motor, but a specified default value to prevent the motors from damaging the robot. Also, the SwingJointNode will update the ROS diagnostic topic for the joint with an error message to alert the higher control layers. This update can be seen using the TriPed-GUI or using a listener for the diagnostic topics. Currently, the system can not exit the error state and needs to be restarted manually.
If the error sum is lower than the specified threshold, then the system will update the ROS diagnostic topics with an OK status message at a specified rate. In the next iteration, the sum decays by a specified amount, if no errors occur, or the errors of the next iteration get added to the sum.
What isn't tracked
While the system can check if the angle is still within bounds, it can not check if the changes between angles are fitting the last motor commands. This means, if the sensor is loosely mounted or too far from the magnet, the actual angle can be very different from the measured angle, while still no error is thrown.
Customisation
The most important things can be customized rather easily, by changing their values in the joints.yaml file. There it is possible to change the spi_error_motor_default_value, which is the default value send to the motors once the system reaches the ERROR state. Currently, it is set to 0, since the motor API uses motor current and not position, and putting current on the motor, while the system is in ERROR state can be dangerous.
Also, the threshold for when the system changes state from OK to ERROR can be modified using the spi_error_treshold parameter. Increasing its value leads to a more lenient error handling and possibly a slower reaction to errors. Decreasing it too much might make the system unusable since some errors in the SPI transfer are common and do not interfere with normal operation.
Other customization can be done by changing the values of the weights of the errors in the SwingJoint::read() function and by changing the rate of decay applied if no errors occur. If needed the rate of the publishing of OK status messages can be changed in the SwingJointNode::main() function. Currently, it is set to 2 Hz, which is the lowest rate, the TriPed GUI will take for updates.
The Documentation of this repository can be seen here.
Error List
| Error name | Cause | Fix | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPI_DEVICE_ERROR | Spi device can't be opened. | Restart controller. | 50 |
| SPI_MODE_ERROR | Mode of spi device can't be set / read. Device usage too high. | Ignore / Check device usage. | 0 |
| SPI_CMD_ERROR | Error bit was set. Last reading may be wrong. | check device usage. | 5 |
| SPI_PARITY_ERROR | Parity of spi message is wrong. Maybe wrong timings for spi transfer. | Check if spi mode is correct. | 5 |
| ANGLE_OUT_OF_BOUNDS_ERROR | Incorrect sensor value! | Check sensor connections! | error threshold |
| JOINT_LIMIT_ERROR | Unfeasible sensor value! | Check sensor position, initialisation and joint limits. | error threshold |